Operating Leverage DOL Formula + Calculator


A higher DOL means that a small change in sales can have a significant impact on your operating income. If you have a small business, you must calculate the degree of operating leverage to maintain the bookkeeping of transactions. However, in DOL, the derived proportion of sales only works with a limited range, which may become a problem. If sales increase beyond this limit, a business may increase its production resulting in a rise in the fixed cost structure. Conversely, Walmart retail stores have low fixed costs and large variable costs, especially for merchandise. Because Walmart sells a huge volume of items and pays upfront for each unit it sells, its cost of goods sold increases as sales increase.
Operating Leverage: What It Is, How It Works, How to Calculate
By calculating the DOL, you can identify areas where cost reductions can have the most significant impact on profitability. Use the calculator to pinpoint cost control opportunities and streamline your operations. A lower DOL indicates that your profits are less sensitive to sales changes, allowing for more flexibility in pricing and promotions. Use the calculator to fine-tune your sales approach for maximum profitability. On the contrary, companies having low operating leverage may find it effortless to earn a profit when trading with lower sales. Next, if the case toggle is set to “Upside”, we can see that revenue is growing 10% each year and from Year 1 to Year 5, and the company’s operating margin expands from 40.0% to 55.8%.
Get in Touch With a Financial Advisor
- This means that changes in sales have a less dramatic impact on operating income.
- A high DOL can be good if a company is expecting an increase in sales, as it will lead to a corresponding operating income increase.
- Many small businesses have this type of cost structure, and it is defined as the change in earnings for a given change in sales.
- Instead, the decisive factor of whether a company should pursue a high or low degree of operating leverage (DOL) structure comes down to the risk tolerance of the investor or operator.
Because retailers sell a large volume of items and pay upfront for each unit sold, COGS increases as sales increase. The Degree of Operating Leverage Calculator is a valuable tool for financial analysts, investors, and business owners. It provides insights into a company’s sensitivity to changes in its operating income due to variations in sales. By understanding the DOL formula and using the calculator effectively, stakeholders can make informed decisions about investments and business strategies. High DOL values suggest potential for increased profits but also increased risk, while low DOL values imply stability but limited profit growth.
Example Calculation of DOL
We put this example on purpose because it shows us the worst and most confusing scenario for the operating leverage ratio. Variable costs vary with production levels, such as raw materials and labor. Fixed costs remain constant regardless of production levels, such as rent and insurance. Alternatively, a company with a low DOL typically spends more money on fixed assets to increase its sales. Chartered accountant Michael Brown is the founder and CEO of Double Entry Bookkeeping.
Great! The Financial Professional Will Get Back To You Soon.
If a company has high operating leverage, each additional dollar of revenue can potentially be brought in at higher profits after the break-even point has been exceeded. As said above, we can verify that a positive operating leverage ratio does not always mean that the company is growing. Actually, it can mean that the business is deteriorating or going through a bad economic cycle like the one from the 2nd quarter of 2020. The following information pertains to last week’s operations of XYZ Company. DCL is a more comprehensive measure of a company’s risk because it takes into account both sales and financial leverage. We’ll go over exactly what it is, the formula used to calculate it, and how it compares to the combined leverage.
How it Calculates:
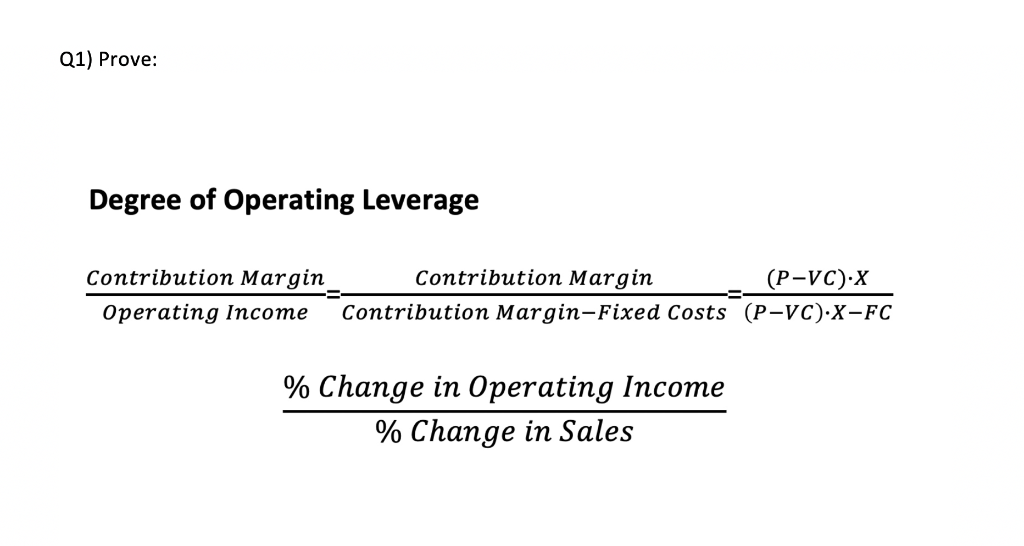
Secondly enter the quantity of units sold, unit selling price and unit cost price information for each business. The degree of operating leverage calculator works out the contribution margin per unit sold. The higher the degree of operating leverage (DOL), the more sensitive a company’s earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) are to changes in sales, assuming all other variables remain constant. The DOL ratio helps analysts determine what the impact of any change in sales will be on the company’s earnings. In the base case, the ratio between the fixed costs and the variable costs is 4.0x ($100mm ÷ $25mm), while the DOL is 1.8x – which we calculated by dividing the contribution margin by the operating margin.
If all goes as planned, the initial investment will be earned back eventually, and what remains is a high-margin company with recurring revenue. In this best-case scenario of a company with a high DOL, earning outsized profits on each incremental sale becomes plausible, but this type of outcome is never guaranteed. When a company’s revenue increases, having a high degree of leverage tends to be beneficial to its profit margins and FCFs. Or, if revenue fell by 10%, then that would result in a 20.0% decrease in operating income. Suppose the operating income (EBIT) of a company grew from 10k to 15k (50% increase) and revenue grew from 20k to 25k (25% increase).
A high DOL indicates that a company has a larger proportion of fixed costs compared to variable costs. This suggests that the company’s earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) are highly sensitive to changes in sales. When sales increase, a company with high operating leverage can see significant boosts what is hire purchase in operating income due to the fixed nature of its costs. Conversely, if sales decline, the company still needs to cover substantial fixed costs, which can significantly hurt profitability. The Degree of Operating Leverage (DOL) measures how a company’s operating income responds to changes in sales.
However, companies rarely disclose an in-depth breakdown of their variable and fixed costs, which makes usage of this formula less feasible unless confidential internal company data is accessible. On that note, the formula is thereby measuring the sensitivity of a company’s operating income based on the change in revenue (“top-line”). So, whether you’re a seasoned financial pro or a business owner looking to optimize profitability, keep this guide handy. With the right tools and understanding, you can leverage your fixed costs to drive financial success.
The calculator will reveal that the Degree of Operating Leverage (DOL) for this scenario is 2. This means that a 1% change in sales will result in a 2% change in operating income. The degree of operating leverage can never be harmful since it is a two-positive numbers ratio, i.e., sales and operating income. Moreover, the negative operating leverage implies that the operating income decreases as the revenue increases, which is inconsistent with the traditional definition of operating leverage. In contrast, companies with low operating leverage have cost structures comprised of comparatively more variable costs that are directly tied to production volume.